Java Scanner is used to store variables and string you inputted in the console. For example, the program requires you to put/type any number. The string or the number you inputted in the console is being stored by the the Scanner. So that later your program can access the data you inputted. In able to use the Scanner you must import it to your Program (at the top part of your program see the first picture below) just type "import java.util.Scanner;".
Now, you have imported the Scanner in your program, you can now assign a name into that Scanner just type the word "Scanner scannername = new Scanner(System.in);". Note that you can have any name for the scannername. Any character is qualify for a ScannerName.
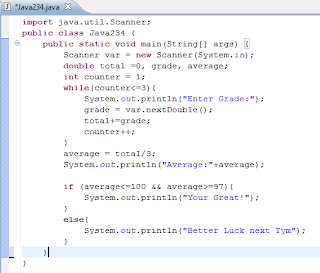
In order to access information inside that scanner, first call the variable you stored to that scanner, put the equal sign then second put the scannername ,put the dot symbol (.) and type one of the ff keyword
nextLine( ); ---> If variable is a String or a Character.
next( ); ----> If you want to leave the cursor the last letter of the String.
nextInt( ); ---> If the variable is an Integer.
nextDouble( ); ---> If the variable is a float/double Value.
(ex. variable = scannername.nextInt( ); if the variable is an Integer)
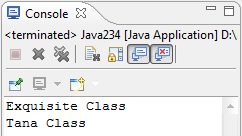
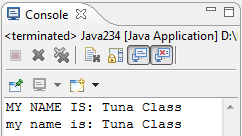
For example, a program that will ask you to enter your name and then it will output the greeting "Hello " plus your name. Later, your name will be stored in the Scanner then the program will access/process the information you inputted and add the word "Hello " to it. Consider this example.